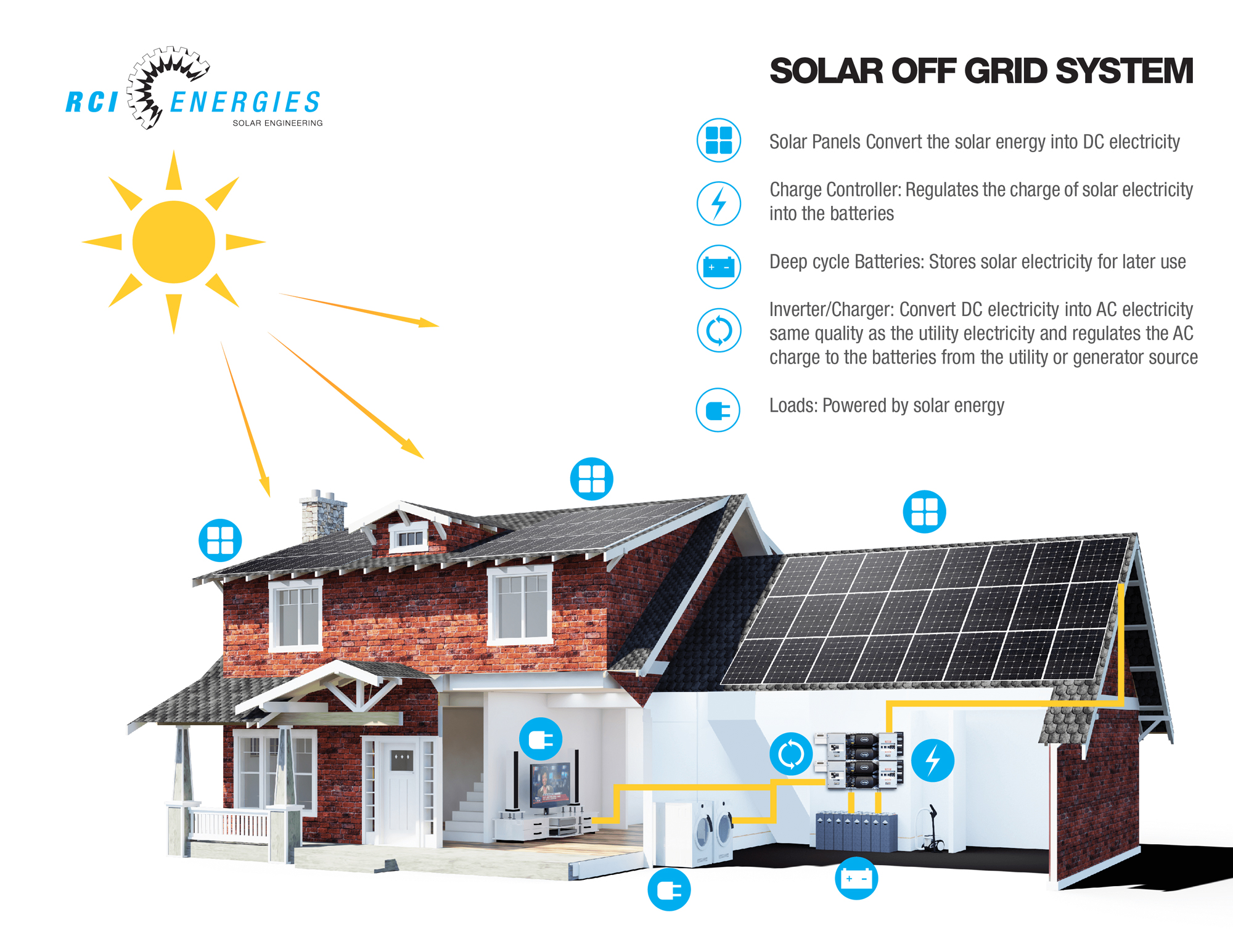
Off grid residential solar power systems – Off-grid residential solar power systems empower homeowners to embrace energy independence and live sustainably. These systems harness the sun’s abundant energy, offering numerous benefits and the potential for significant savings.
Understanding the components, design considerations, and financial aspects of off-grid solar systems is crucial for making informed decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of these systems, providing valuable insights for homeowners seeking to embark on their off-grid solar journey.
Overview of Off-Grid Residential Solar Power Systems
Off-grid residential solar power systems are standalone systems that provide electricity to homes and businesses in remote areas or where grid connection is impractical or unavailable. These systems typically consist of solar panels, batteries, charge controllers, and inverters.
Off-grid solar systems offer several benefits, including energy independence, reduced electricity costs, and environmental sustainability. However, they also have limitations, such as higher upfront costs, limited power availability during periods of low sunlight, and the need for regular maintenance.
Real-Life Examples of Off-Grid Solar Installations
- The Solar Homestead in Oregon, USA, is a fully off-grid home powered by a 10 kW solar system with a 48-volt battery bank.
- The Off-Grid Project in Australia is a community of off-grid homes powered by solar and wind energy.
- The EcoVillage in Costa Rica is a sustainable community that uses off-grid solar power to meet its electricity needs.
Components of an Off-Grid Solar Power System
An off-grid solar power system consists of several essential components that work together to generate, store, and convert electricity for residential use. These components include solar panels, batteries, inverters, and charge controllers, each playing a crucial role in the system’s functionality.
Solar Panels
Solar panels are the heart of an off-grid solar system, responsible for converting sunlight into electricity. They consist of photovoltaic cells that absorb sunlight and generate direct current (DC) electricity. The number and size of solar panels required depend on the energy needs of the household and the amount of sunlight available at the location.
Batteries
Batteries store the DC electricity generated by the solar panels. They provide a backup power source during periods of low sunlight or high energy consumption. The capacity and type of batteries selected depend on the daily energy usage, the number of days of autonomy desired, and the discharge depth requirements.
Inverters
Inverters convert the DC electricity from the solar panels or batteries into alternating current (AC) electricity. AC electricity is used to power most household appliances and devices. The size and type of inverter required depend on the total load capacity and the specific appliances being used.
Charge Controllers
Charge controllers regulate the flow of electricity between the solar panels, batteries, and inverter. They prevent overcharging of the batteries and ensure optimal charging efficiency. Charge controllers also protect the system from overcurrent and short circuits.
Get the entire information you require about different types of ecotourism on this page.
Design and Installation Considerations
Designing and installing an off-grid residential solar power system requires careful planning and attention to detail. Factors such as energy consumption, system size, and site conditions play a crucial role in determining the system’s effectiveness and efficiency.
Site Assessment
A thorough site assessment is essential to evaluate the suitability of the location for an off-grid solar system. This includes analyzing factors such as:
- Sun exposure: Determine the amount of sunlight available throughout the year, considering factors like shading from trees or buildings.
- Roof orientation and pitch: Assess the orientation and pitch of the roof to optimize solar panel placement for maximum sunlight exposure.
- Load analysis: Estimate the energy consumption of the household to determine the size and capacity of the solar system required.
- Battery storage capacity: Calculate the amount of battery storage needed to meet energy demands during periods of low sunlight or high usage.
- Electrical infrastructure: Ensure the existing electrical infrastructure can support the solar system and handle the additional electrical load.
System Design
Based on the site assessment, the solar system can be designed to meet the specific energy needs of the household. This involves:
- Solar panel selection: Choose solar panels with appropriate efficiency and power output to generate the required amount of electricity.
- Battery selection: Select batteries with sufficient capacity and discharge rate to store excess solar energy and provide backup power during outages.
- Inverter selection: Determine the type and size of inverter needed to convert DC power from the solar panels into AC power for household use.
- Wiring and electrical components: Plan the wiring and electrical components, including cables, connectors, and safety devices, to ensure efficient and safe operation.
Installation, Off grid residential solar power systems
The installation of an off-grid solar system should be carried out by qualified professionals. The process typically involves:
- Site preparation: Prepare the roof or ground-mounted structure for the solar panels.
- Panel mounting: Securely mount the solar panels on the prepared structure.
- Electrical connections: Connect the solar panels, batteries, inverter, and other electrical components to complete the system.
- System testing and commissioning: Thoroughly test the system to ensure it is functioning correctly and meeting performance expectations.
Optimization
To maximize system performance and energy output, consider the following tips:
- Monitor system performance: Regularly monitor the system’s output, battery levels, and energy consumption to identify any potential issues or areas for improvement.
- Keep panels clean: Ensure the solar panels are kept clean to maximize sunlight absorption.
- Use energy-efficient appliances: Opt for energy-efficient appliances and practices to reduce overall energy consumption.
- Consider additional energy sources: Explore the possibility of integrating other renewable energy sources, such as wind or hydropower, to supplement the solar system.
Cost and Return on Investment
The cost of installing an off-grid solar system varies depending on the size and complexity of the system, as well as the location and availability of labor. However, as a general rule of thumb, you can expect to pay between $15,000 and $30,000 for a complete system.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about how to make tourism sustainable.
This includes the cost of the solar panels, inverter, batteries, wiring, and installation.The return on investment (ROI) for off-grid solar systems can be significant. In areas with high energy costs, you can save thousands of dollars on your electric bill each year.
Additionally, many governments offer financial incentives for the installation of solar panels, which can further reduce the cost of the system.When compared to other energy sources, off-grid solar systems are a cost-effective option in the long run. While the initial investment may be higher than for other energy sources, the savings on energy costs over time will typically outweigh the initial cost.
Discover the crucial elements that make how does ecotourism work the top choice.
Cost of Installation
The cost of installing an off-grid solar system can be broken down into three main components:
- Equipment:This includes the cost of the solar panels, inverter, batteries, wiring, and other components.
- Labor:This includes the cost of hiring a qualified electrician to install the system.
- Maintenance:This includes the cost of定期维护the system, such as cleaning the solar panels and replacing the batteries.
The cost of equipment will vary depending on the size and complexity of the system. However, as a general rule of thumb, you can expect to pay between $5,000 and $10,000 for a complete system.The cost of labor will also vary depending on the location and availability of qualified electricians.
However, as a general rule of thumb, you can expect to pay between $5,000 and $10,000 for labor costs.The cost of maintenance will be relatively low, typically only a few hundred dollars per year.
Return on Investment
The return on investment (ROI) for off-grid solar systems can be significant. In areas with high energy costs, you can save thousands of dollars on your electric bill each year. Additionally, many governments offer financial incentives for the installation of solar panels, which can further reduce the cost of the system.The ROI for off-grid solar systems will vary depending on the following factors:
- The cost of electricity in your area
- The amount of sunlight your property receives
- The size of your solar system
- The efficiency of your solar panels
- The cost of financing
If you live in an area with high energy costs and your property receives a lot of sunlight, then you can expect to see a significant ROI on your investment in an off-grid solar system.
Comparison to Other Energy Sources
When compared to other energy sources, off-grid solar systems are a cost-effective option in the long run. While the initial investment may be higher than for other energy sources, the savings on energy costs over time will typically outweigh the initial cost.The following table compares the cost of off-grid solar systems to other energy sources:| Energy Source | Upfront Cost | Ongoing Costs ||—|—|—|| Off-grid solar | $15,000-$30,000 | $0-$500/year || Grid-tied solar | $10,000-$20,000 | $0-$100/year || Diesel generator | $5,000-$10,000 | $1,000-$2,000/year || Propane generator | $3,000-$5,000 | $500-$1,000/year |As you can see, off-grid solar systems have a higher upfront cost than other energy sources.
However, the ongoing costs are much lower, which makes them a more cost-effective option in the long run.
Obtain a comprehensive document about the application of origin of ecotourism that is effective.
Case Studies and Best Practices: Off Grid Residential Solar Power Systems
Showcase successful case studies of off-grid solar systems in different regions and applications. Identify best practices for designing, installing, and maintaining off-grid solar systems. Discuss the latest advancements and emerging trends in off-grid solar technology.
Case Studies
- A case study of an off-grid solar system powering a remote cabin in Alaska, highlighting the challenges of designing a system for extreme weather conditions.
- A case study of an off-grid solar system powering a small village in Africa, showcasing the benefits of solar energy in rural electrification.
- A case study of an off-grid solar system powering a sustainable home in California, demonstrating the integration of solar energy into modern architecture.
Best Practices
Best practices for designing off-grid solar systems include:
- Conducting a thorough energy audit to determine the electrical load requirements.
- Selecting high-quality components that are designed for off-grid use.
- Properly sizing the solar array to meet the energy needs of the system.
Best practices for installing off-grid solar systems include:
- Following manufacturer’s instructions and adhering to local building codes.
- Using qualified installers with experience in off-grid solar systems.
- Properly grounding the system to ensure safety.
Best practices for maintaining off-grid solar systems include:
- Regularly cleaning the solar panels to maintain optimal performance.
- Inspecting the system components periodically for any signs of damage or wear.
- Replacing batteries as needed to ensure the system’s reliability.
Advancements and Trends
The latest advancements and emerging trends in off-grid solar technology include:
- The development of more efficient solar panels that produce more power with less space.
- The use of advanced battery technologies that store more energy for longer periods of time.
- The integration of smart grid technologies that allow off-grid solar systems to interact with the grid when necessary.
Final Summary
Off-grid residential solar power systems offer a path towards energy autonomy, environmental sustainability, and long-term cost savings. By carefully considering the factors discussed in this guide, homeowners can design and implement systems that meet their specific energy needs and financial goals.
As technology continues to advance, off-grid solar systems will undoubtedly play an increasingly significant role in the future of residential energy.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the key components of an off-grid solar system?
The essential components include solar panels, batteries, inverters, and charge controllers, each playing a vital role in generating, storing, and managing solar energy.
How do I determine the size of my off-grid solar system?
System size depends on energy consumption, available sunlight, and desired level of energy independence. A qualified solar installer can conduct an energy audit to assess your needs and design an optimal system.
What are the financial benefits of going off-grid with solar?
Off-grid solar systems can reduce or eliminate electricity bills, provide protection against rising energy costs, and potentially increase property value.