With vegetarian nutrition chart at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling semrush author style filled with unexpected twists and insights.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
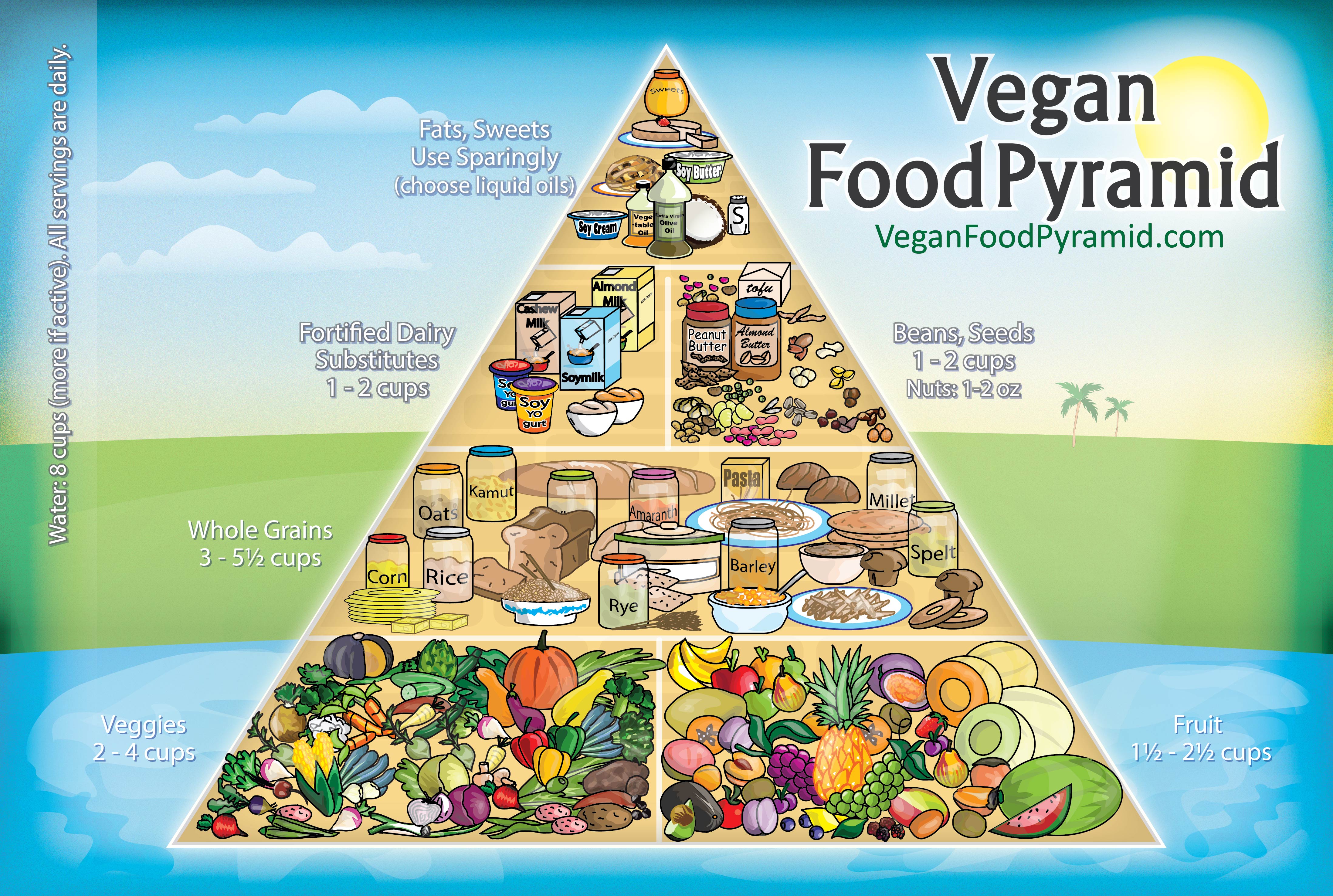
Essential Nutrient Profile
A vegetarian diet offers a comprehensive array of essential nutrients, including protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Understanding the recommended daily intake for each nutrient is crucial for ensuring a balanced and nutritious diet.
This chart provides a detailed overview of the essential nutrients and their recommended daily intake, along with insights into how a vegetarian diet can fulfill these requirements:
Protein
- Recommended daily intake: 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight
- Vegetarian sources: Legumes (beans, lentils), tofu, tempeh, nuts, seeds, quinoa
- Complete proteins (containing all essential amino acids): Soy products, quinoa, chia seeds
Carbohydrates
- Recommended daily intake: 45-65% of total calories
- Vegetarian sources: Whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, oats), fruits, vegetables
- Complex carbohydrates: Provide sustained energy and fiber
Fats
- Recommended daily intake: 20-35% of total calories
- Vegetarian sources: Olive oil, avocado, nuts, seeds
- Healthy fats: Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats
Vitamins
- Vitamin B12: Required for red blood cell production and nervous system function. Vegetarian sources: Fortified foods (plant-based milk, cereals), nutritional yeast
- Vitamin D: Essential for bone health. Vegetarian sources: Sunlight exposure, fortified foods (plant-based milk, cereals)
- Iron: Necessary for oxygen transport. Vegetarian sources: Legumes, leafy green vegetables, fortified cereals
Minerals
- Calcium: Vital for bone health. Vegetarian sources: Leafy green vegetables, fortified plant-based milk, tofu
- Iron: Essential for oxygen transport. Vegetarian sources: Legumes, leafy green vegetables, fortified cereals
- Zinc: Supports immune function and cell growth. Vegetarian sources: Legumes, nuts, seeds
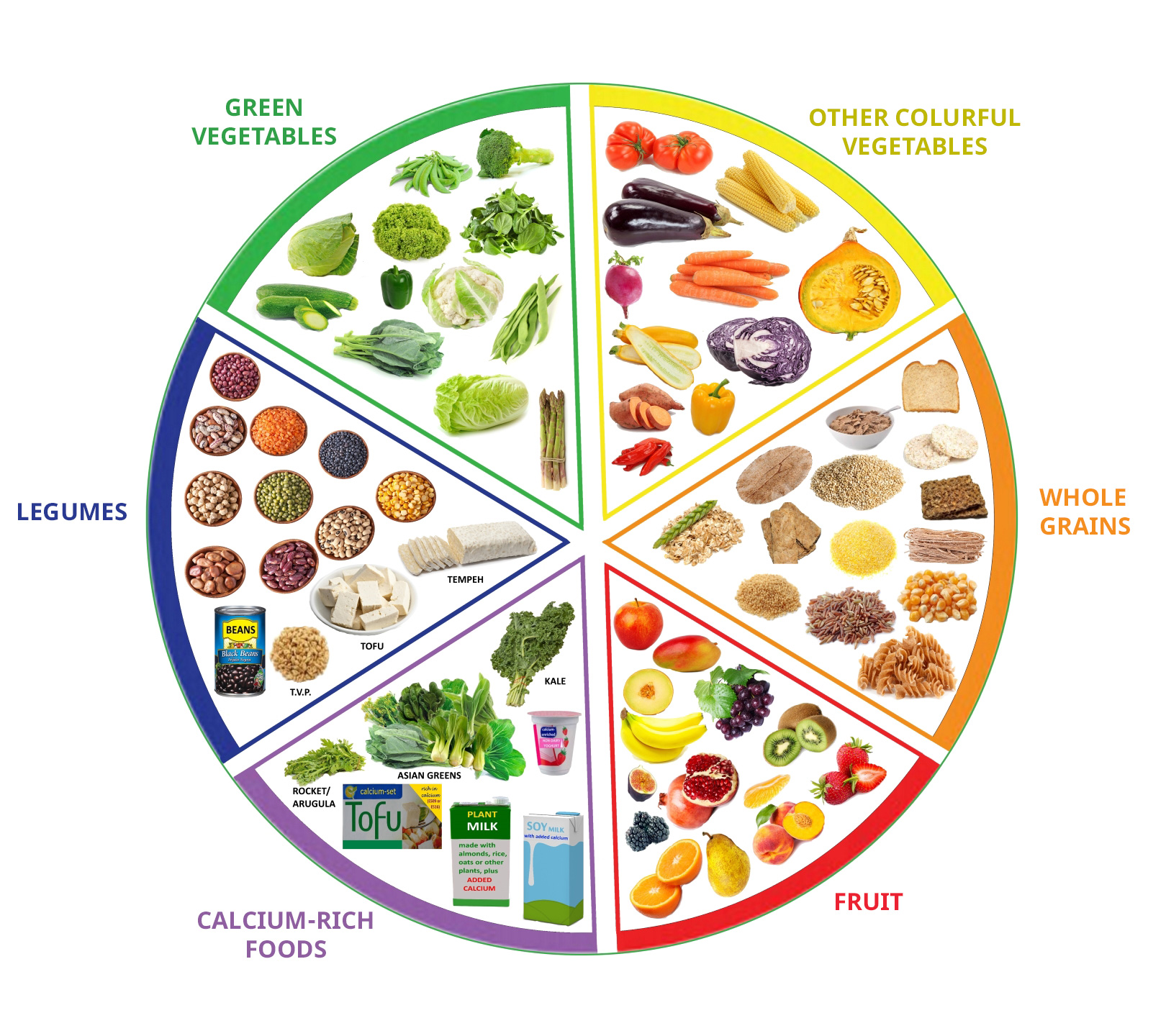
Food Sources for Key Nutrients
For vegetarians, ensuring adequate intake of essential nutrients is crucial. Plant-based foods provide a rich source of these nutrients, and understanding their sources is vital for maintaining a healthy and balanced diet.
The following table highlights plant-based food sources that are excellent providers of key nutrients for vegetarians:
Protein
- Legumes (beans, lentils, peas)
- Tofu and tempeh
- Nuts and seeds
- Quinoa
Iron
- Leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale, collard greens)
- Beans and lentils
- Fortified cereals
- Dried fruits (raisins, apricots)
Calcium
- Leafy green vegetables (collard greens, kale)
- Fortified plant-based milk (soy milk, almond milk)
- Tofu
- Tahini
Vitamin B12
- Fortified plant-based milk and yogurt
- Nutritional yeast
- Certain mushrooms (shiitake, oyster)
Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Vegetarian nutrition chart
- Flaxseed and chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Algae oil supplements
Meal Planning and Recipe Ideas
Meal planning for vegetarians requires careful consideration to ensure a balanced intake of nutrients. Incorporate a variety of plant-based foods from all food groups to meet nutritional needs. Plan meals around whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Include fortified foods, such as plant-based milk and yogurt, to enhance nutrient intake.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about 17 foot boats for sale.
Creative and Diverse Recipe Ideas
Vegetarian meals can be flavorful and satisfying. Experiment with different cuisines and cooking techniques to create a diverse range of dishes. Try incorporating tofu, tempeh, seitan, and lentils into your meals as protein sources. Explore plant-based alternatives for dairy products, such as almond milk, soy cheese, and coconut yogurt.
Utilize herbs, spices, and seasonings to enhance the flavors of your dishes.
Healthy Cooking Techniques
Adopting appropriate cooking techniques is essential for preserving the nutritional value and enhancing the flavor of plant-based ingredients in a vegetarian diet. Various healthy cooking methods, such as steaming, roasting, and stir-frying, can help retain nutrients while creating delicious and satisfying meals.
When investigating detailed guidance, check out boat sales tax now.
Steaming
- Steaming involves cooking food over boiling water, allowing heat and moisture to gently penetrate the ingredients.
- This method preserves vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, as the food is not exposed to high temperatures or excessive water.
- Steaming is particularly suitable for delicate vegetables, such as broccoli, carrots, and leafy greens, as it retains their vibrant colors and textures.
Roasting
- Roasting involves cooking food in an oven at high temperatures, creating a caramelized exterior and tender interior.
- This method enhances the natural flavors of vegetables, such as potatoes, carrots, and bell peppers, while promoting the formation of beneficial compounds.
- Roasting is also an effective way to prepare tofu, tempeh, and seitan, providing a crispy texture and rich flavor.
Stir-Frying
- Stir-frying involves cooking food quickly in a hot pan or wok, using a small amount of oil.
- This method helps preserve nutrients by minimizing cooking time and prevents overcooking, which can degrade vitamins and minerals.
- Stir-frying is ideal for vegetables, such as broccoli, carrots, and onions, as well as tofu, tempeh, and seitan, resulting in a flavorful and colorful dish.
Vegetarian Nutrition Myths and Facts
Vegetarian diets have been associated with various misconceptions and myths. This section aims to address these common beliefs and provide evidence-based information to dispel them, highlighting the benefits of a well-planned vegetarian diet.
One prevalent myth is that vegetarians lack sufficient protein. However, plant-based foods such as beans, lentils, tofu, and nuts are excellent sources of protein. Studies have shown that vegetarians can meet their protein requirements by consuming a variety of plant-based sources.
Check eliminator boats for sale by owner to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Another common misconception is that vegetarians are at risk of vitamin B12 deficiency. Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal products, but it can also be obtained from fortified foods like cereals, nutritional yeast, and plant-based milks. Regular consumption of these foods can ensure adequate vitamin B12 intake for vegetarians.
In this topic, you find that pursuit boats for sale by owner is very useful.
Iron Absorption
Some people believe that vegetarians have lower iron absorption compared to meat-eaters. While it is true that heme iron from animal products is more readily absorbed than non-heme iron from plant sources, vegetarians can enhance iron absorption by consuming iron-rich foods alongside vitamin C-rich fruits and vegetables.
Calcium Intake
Another myth is that vegetarians may not get enough calcium. However, dairy products are not the only source of calcium. Leafy green vegetables, fortified plant-based milks, and tofu are all good sources of calcium for vegetarians.
Overall Health Benefits
Contrary to popular belief, vegetarian diets are not inherently unhealthy. In fact, well-planned vegetarian diets have been linked to various health benefits, including reduced risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Vegetarian diets are typically high in fiber, antioxidants, and phytochemicals, which contribute to overall well-being.
End of Discussion: Vegetarian Nutrition Chart
The content of the concluding paragraph that provides a summary and last thoughts in an engaging manner
FAQ Overview
What are the essential nutrients for vegetarians?
Protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals are essential nutrients for vegetarians.
How can vegetarians get enough protein?
Vegetarians can get enough protein from plant-based sources such as beans, lentils, tofu, and nuts.
What are some good sources of iron for vegetarians?
Good sources of iron for vegetarians include leafy green vegetables, beans, and lentils.
How can vegetarians get enough vitamin B12?
Vegetarians can get enough vitamin B12 from fortified foods or supplements.